In this article, I will be explaining how to create a Spring Boot REST service that produces an XML output.
Project Creation and Setup
Step 1 – Create a new Maven Project (Refer to this blog post). This should create a project as shown below:
Step 2 - Add the Spring Boot and Jackson dependency. So, your the pom.xml file should be similar to the following:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.learnjava</groupId>
<artifactId>learnjava-springboot-xmloutput-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
</project>
Writing Code
Step 3 - Create a Book class as follows:
package com.learnjava.springbootxmldemo.book;
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private String author;
//constructor, getters and setters
}
This class represents a Book. It has fields corresponding to id, name and author.
Step 4 - Create a BookController class as follows:
package com.learnjava.springbootxmldemo.book;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class BookController {
@GetMapping(value="/books",produces = { "application/xml", "text/xml" })
public List<Book> getAllBooks(){
//Returns hardcoded data, a real world application would return from the database
List<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>();
books.add(new Book(1,"Emma", "Jane Austen"));
books.add(new Book(2,"Harry Potter", "JK Rowling"));
books.add(new Book(3,"The Partner", "John Grisham"));
return books;
}
@GetMapping(value="/book", produces = { "application/xml", "text/xml" })
public Book getBook(){
//Returns hardcoded data, a real world application would return from the database
return new Book(1,"Emma", "Jane Austen");
}
}
This is a Controller class and specifies the methods that handle client requests. . It has the RestController annotation specified.
It includes the following methods:
getAllBooks
- The GetMapping annotation is specified on this method. This specifies that this method maps to the /books URL and that it produces an XML output
- The method simply creates a List of type Book, adds some Book objects to it and returns it. A real-world application will typically query a database and obtain Book objects.
getBook
- Like getAllBooks, this method has the GetMapping annotation
- It returns a single Book object
Step 5 - Create a Main class as follows:
package com.learnjava.springbootxmldemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
}
This is the starting point of our Spring Boot application as explained here.
Running the application
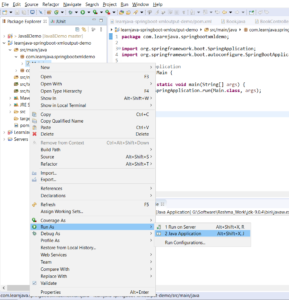
Step 6 - Run Main.java as a Java application as shown below:
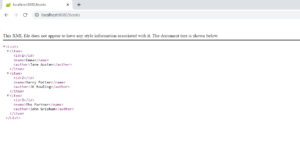
Step 7 - Open a browser window. Type http://localhost:8080/books/ . This displays the following XML output:
You can download the source code for this project via the Github repository here.
Conclusion
So, in this article, we saw how to create a Spring Boot application that produces an XML output.